This preview shows page 27 - 31 out of 146 pages. It interfaces with telephone company zone offices controls call processing provides operation and maintenance and handles billing activities.
Out of total radio channels say 416 available for a cellular coverage area few channels say 21 are designated for setting up connections and are called as set-up-channels.

. Due to their lower cost and higher efficiency service providers have used aggressive pricing tactics to encourage user migration from analog to digital systems. Each cell has its base station and masts and all the calls made or received inside that cell are routed through them. Co-Channel Interference and Cell Separation.
It is a computerized center that is responsible for connecting calls recording call information and billing. By limiting the coverage area to within the boundary of the cell the channel groups may be reused to cover different cells. A Mobile Station MS A mobile station is basically a mobilewireless device that contains a control unit a transceiver and an antenna system for data and voice transmission.
Known as the powerhouse of the cell the mitochondrion plural. Neighboring cells are assigned different channel groups. When a mobile moves into a different cell while a conversation is in progress the MSC automatically transfers the call to a new channel belonging to the new base station.
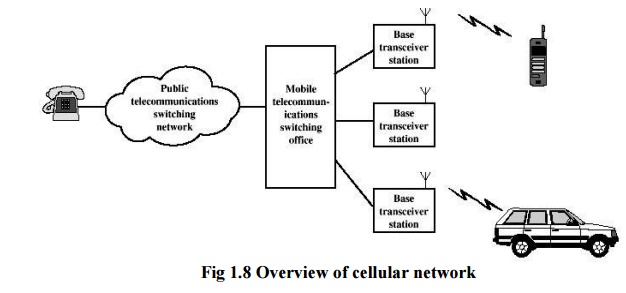
Cellular Network is formed of some cells cell covers a geographical region has a base station analogous to 80211 AP which helps mobile users attach to network and there is an air-interface of physical and link layer protocol between mobile and base station. Six basic components of Cellular Systems. The HLR home location register and VLR visitor location register are.
Both tower and antenna are a part of the BTS while all associated electronics are contained in the BSC. Operation of Cellular Systems The Operation of a cellular system can be divided into four parts besides a handoff procedure. All the functions together make a complete mobile cellular system.
This cellular approach introduces many difficulties such as how to avoid interference or how to hand-over from one. The specifications must protect the value of operators investments in spectrum by managing unwanted emissions and incoming interference ensuring that devices and networks behave in a predictable manner and ensuring a basic level of efficiency in using. Q Co-chl interference reduction factor.
During the cellular respiration a usable form of energy is produced from precursor molecules like sugars and other carbohydrates. A Mobile Station MS A mobile station is basically a mobilewireless device that contains a control unit a transceiver and an antenna system for data and voice transmission. Maximum Number of Calls Per Hour Per Cell.
Mitochondria is the double-membraned organelle where the process of cellular respiration takes place. Each cellular base station is allocated a group of radio channels within a small geographic area called a cell. Cellular Systems 26 Operation subsystem The OSS Operation Subsystem enables centralized operation management and maintenance of all GSM subsystems.
The network is distributed over land areas called cells each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver. The switching office the central coordinating element for all cell sites contains the cellular processor and cellular switch. Six basic components of Cellular Systems.
All these base stations are connected to Mobile. Cells enable the system to handle many more calls at once because each cell uses the same set of frequencies as its neighboring cells. Maximum Number of Frequency Channels Per Cell.
All cellular systems being deployed today are digital and these systems provide voice mail paging and e-mail services in addition to voice. The cell system in mobile network and the cell spliting sectoring. Operations of Cellular Systems can be categorized as.
Each cell is served by its own antenna and a base station consisting of transmitter receiver and control unit. Describe the principle of Operation of cellular mobile system and explain the cellular Concept with neat diagram. Different data rates for voice and data original standard data service circuit switched synchronous.
Keep interference levels within tolerable limits. Operation of cellular systems. The operation can be divided into four parts and a handoff procedure.
Deployment and operation of cellular systems require carefully deviced radio requirement and conformance specifications. When mobile unit is turned on it scans and selects the strongest setup control channel used for system. The more cells the greater the number of calls that can be made at once.
Base station include an antenna a controller and a number of receivers. Handoff operation identifying a new base station re-allocating the voice and control channels with the new base station. Explain Cell splitting and Concept of frequency channels.
In which direction the cellular system works and how it changes the network from one bast station to another is simply explained. Frequency reuse or frequency planning. Co-chl interference is a function of q DR.
The architecture of most cellular systems can be broken down into the following six components. A cellular system requires a fairly complex infrastructure. COMPONENTS IN CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 3 main components.
Cellular network organization uses low power transmitter 100W or lessThe areas are divided into cells. Wireless communications are especially useful for mobile applications so wireless systems are often designed to cover large areas by splitting them into many smaller cells. A BS consists of a base transceiver system BTS and a BSC.
24 48 or 96 kbits. The radio and high-speed data links connect the three subsystems. This presentation contains the basic of cellular system.
How Hand-off occur between two base station is shown via figure to understand well. Since the cell size is fixed co-channel interference will be independent of power. The operation of a cellular mobile system can be described as five major functionalities and four additional utilities.
Mobile Station MS UE SIM Base Station Subsystem BSS BTS RBS BSC Network and Switching Subsystem NSS MSC VLR HLR 11. A generic block diagram in shown in the figure. The architecture of most cellular systems can be broken down into the following six components.
We assume a cellular system having a cell radius R and Co-channel distance D and the cluster size N. A cellular network or mobile network is a communication network where the link to and from end nodes is wireless. These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice data and other types of content.

Cellular System An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cellular Network An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

0 Comments